
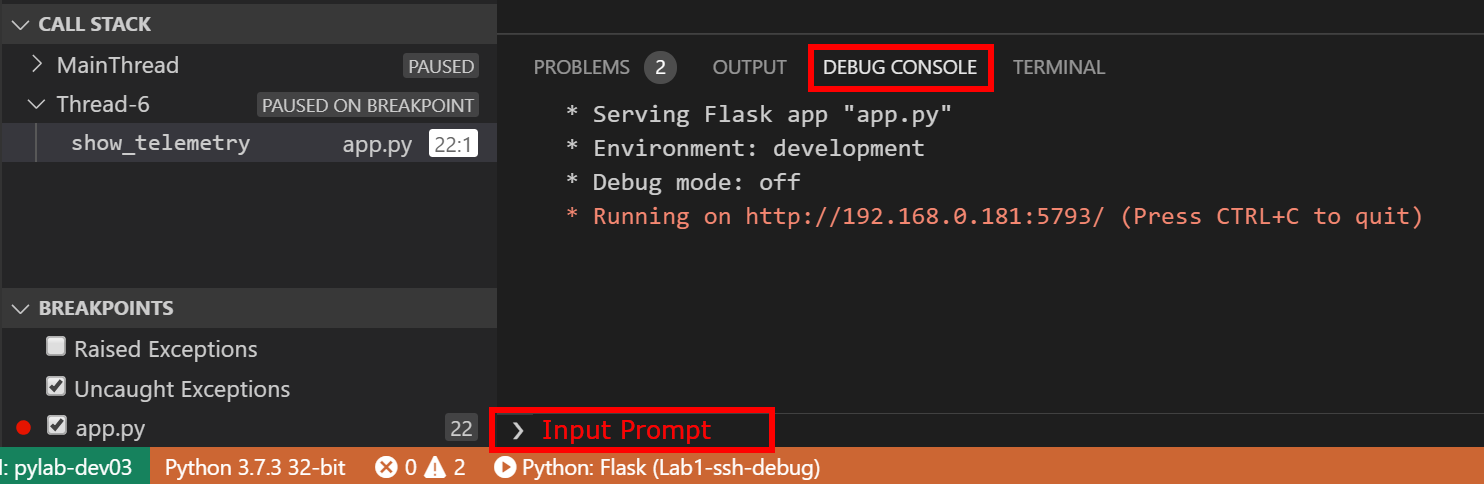
A debugging package installed on the remote application compatible with the IDE.A connection between the server and your local development environment.Remote Debugging ArchitectureĪt a high level, a remote debugging process requires: Alternatively, you can also use your own target Python 3 application, as the libraries you’ll use should be compatible. To download the demo application, follow this link. You’ll use a simple sudoku script as your debugging target.
You will also need Visual Studio Code, preferably with the official Python extension installed. Typically, this is done by writing unit tests that validate the conditions of the original software defect.įor this tutorial, you will need Python 3, venv, Docker Compose and the Flask web framework. Fix and validate: Finally, you need to take steps to change the code and validate that your solution is correct.Analyze the error: Now that you have a better idea of where the error might be located, your next step is to analyze the conditions and the underlying cause to solve the issue.Find the error location: Once you have identified the error correctly, you need to narrow down the code’s location to where the bug is present.
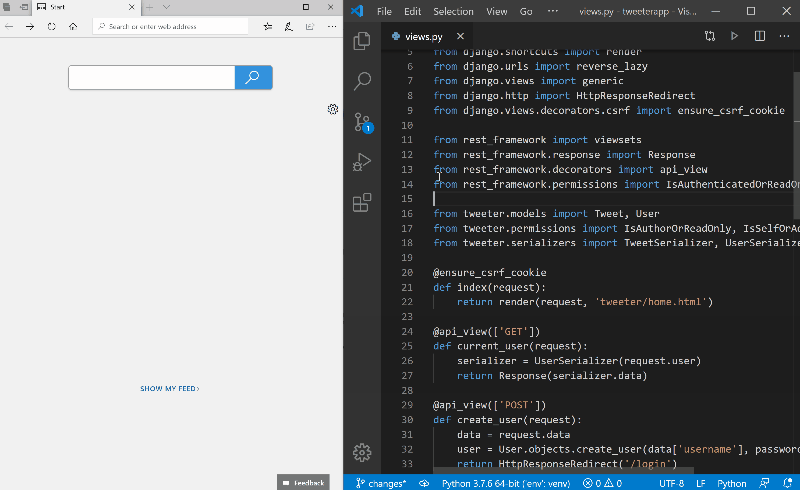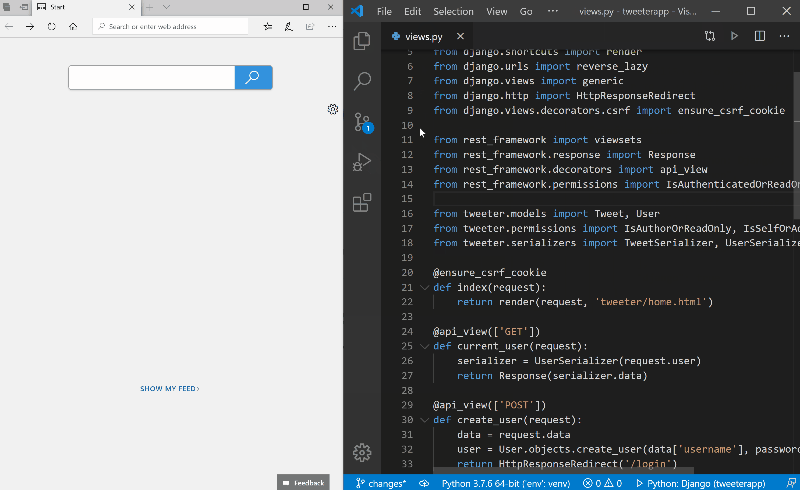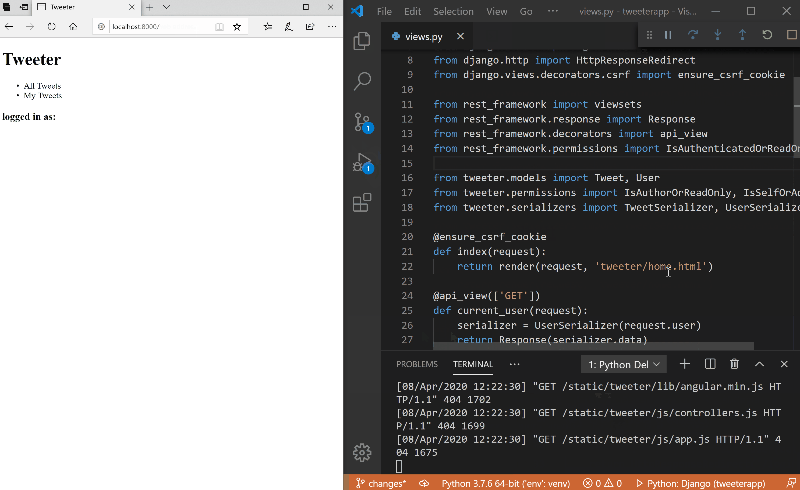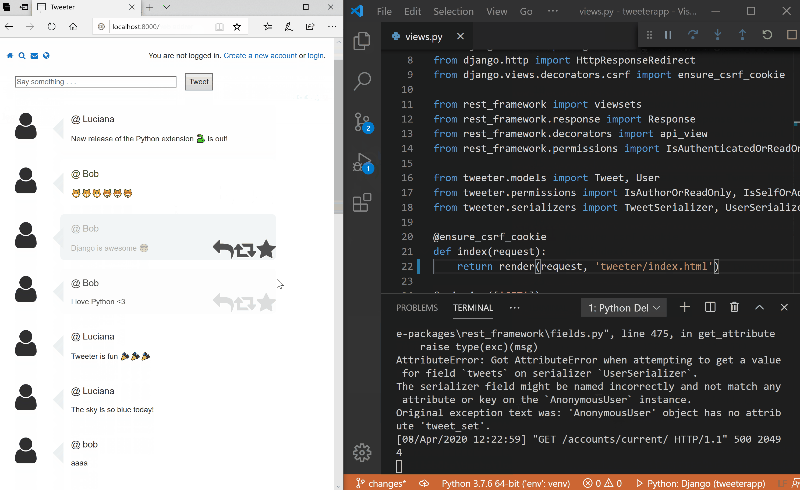
The first step to effective debugging is to make sure you identify the actual error.

This article will focus on a debugging strategy known as forward analysis using remote debugging for Python. To perform remote debugging, you need to be able to remotely connect to a running application from your local development environment. In the simplest terms, remote debugging is debugging an application running in a remote environment like production and staging. Sometimes, remote debugging is necessary. It is a process that can start at any stage of the software development, even as early as the software has been written. Debugging is the process of identifying, analyzing and removing errors in the software.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
